Kompetansemål som RDF
(Competence as RDF, in Norwegian)
See http://grepwiki.udir.no/index.php?title=Kompetansem%C3%A5l_som_RDF
Introduction
General information
(see Example source guidance)
| information to be gathered | details |
|---|---|
| Name / title of source/model and version if applicable | GREP - Norwegian ontology of K12 Curriculum - http://www.udir.no/grep - Wikipedia: http://no.wikipedia.org/wiki/L%C3%A6replaner_i_Norge Wiki for support for developers: http://grepwiki.udir.no/index.php?title=Hovedside Source file in xtm format: http://lkt.udir.no/xtm/Publisert/V1.0/ Example syllabus in RDF http://lkt.udir.no/eksport/rdf.mvc/laereplan/uuidxcx98720dc8-53bd-4fce-b149-5fac1db4b27f |
| Stakeholder | Norwegian Schools Authorities |
| URL of source or stakeholder | http://www.udir.no/grep - http://www.udir.no/Stottemeny/English/Curriculum-in-English/Core-Curriculum-in-five-languages/ |
| Orientation (work, education, etc.) | Curriculum description - with unique codes (URL identifiers) for all subjects in the curriculum. |
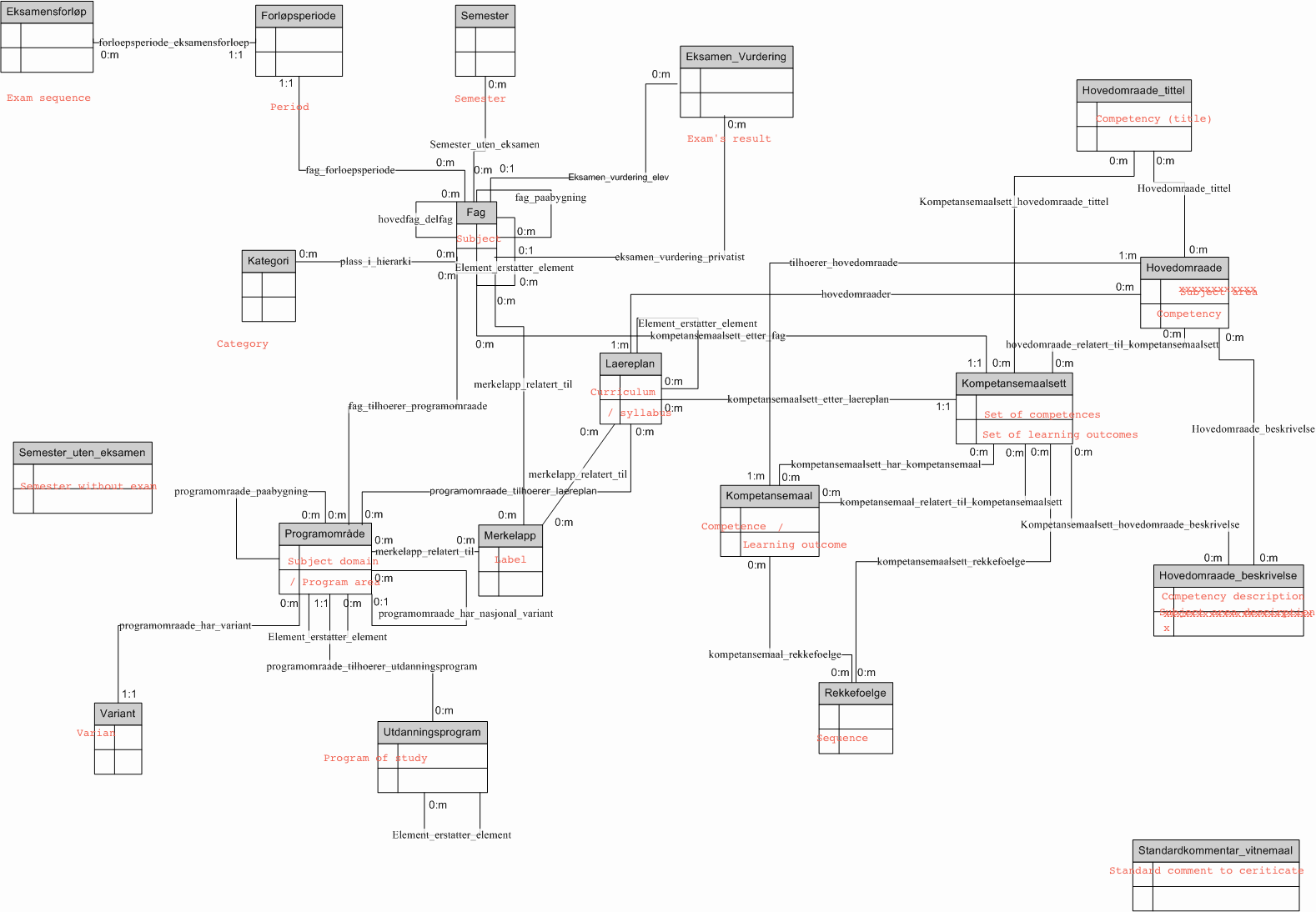
| Explicit model or implicit model? | Explicit - available in Topic Maps format: http://grepwiki.udir.no/images/c/c5/Grep.xtm (need Topic Map viewer to read - or see the model graphic below) |
| Can organisations have competence? | no |
| Number of people currently affected | All schools, local authorities, vendors, pupils.... etc. |
| Sectors covered | School |
| Groups of actual users | |
| Significant use cases | |
| Significant business cases | Alle portals use the Grep as subject classification for search, etc. |
| Sample materials | See http://www.udir.no/grep Since 2006 Utdanningsdirekotoratet stored offers structure, subject number and curricula electronically in a computer system called Grep. The curricula are stored in the data format of topic maps (or RDF). These contain a large number of relations between approximately 300 subjects, 13000 competence, set of competences and a host of other information of 40 different types, such as examination, number of hours, etc. The system has the following purposes:
|
| Key features influencing their uptake of InLOC outputs |
Features
(see the Features page or the separate pages for each feature)
| N | Features | ? | notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 00 | More than one model | 1 | various entities are modelled - see diagram below |
| 01 | Identifiers | 1 | identifiers are given to subjects, competence definitions, ... |
| 02 | Hierarchy (internal) | 1 | subjects; competence sets / competences; etc? |
| 03 | Internal relationships | 1 | subjects can be combined |
| 04 | External relationships | 0 | probably |
| 05 | Conditionality / optionality | ? | |
| 06 | Text syntax | 0 | |
| 07 | Structured identifiers | 0 | probably |
| 08 | Classification | 1 | categories |
| 09 | Level attribution | 1 | through "semester" |
| 10 | Level definition | 0 | |
| 11 | Context | ||
| 12 | Evidence and assessment | 1 | |
| 13 | Extensions | ||
| 14 | Profiles | ||
| 15 | Adaptation | ||
| 16 | Definition by example | 0 | |
| 17 | Learning resources | 0 | learning resources refer to subjects |
| 18 | Learner records | 0 | |
| 19 | Multilinguality | ? | probably just translation? |
Further information
The model graphic representation